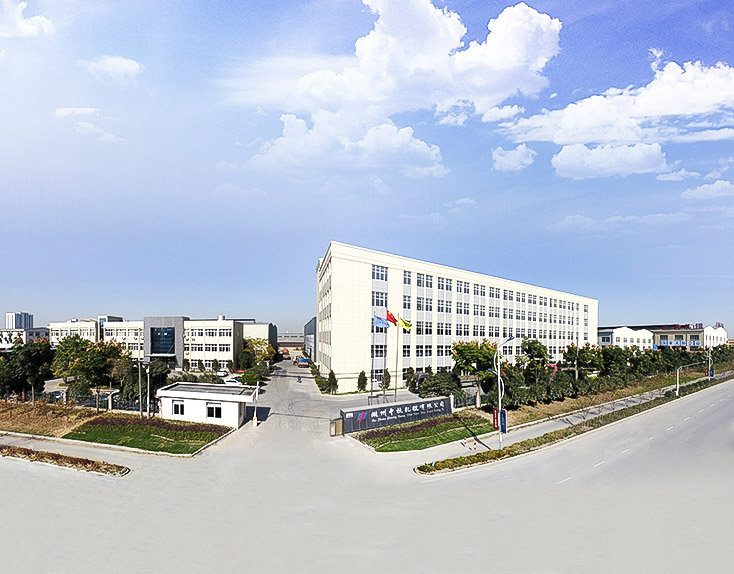
High chromium iron rollers are commonly used in the automotive industry. How are they resistant to high temperatures?
High Chromium iron rollers exhibit resistance to high temperatures primarily due to their specific alloy composition and microstructure. Here are the key factors that contribute to their high temperature resistance:
- Alloy Composition: High Chromium iron rollers typically contain a significant amount of chromium (often around 18% to 30%) along with other alloying elements such as nickel, molybdenum, and sometimes vanadium. Chromium plays a crucial role in enhancing the oxidation resistance of the material at elevated temperatures. It forms a stable oxide layer (chromia scale) on the surface of the rollers, which acts as a barrier to further oxidation and helps protect the underlying material from degradation.
- Oxidation Resistance: The chromia scale formed on the surface of High Chromium iron rollers provides excellent oxidation resistance at high temperatures. This scale adheres tightly to the surface, preventing the loss of material and maintaining the integrity of the roller under prolonged exposure to heat.
- Thermal Stability: High Chromium iron rollers have good thermal stability, meaning they can maintain their mechanical properties and dimensional stability at high temperatures. This is essential in automotive manufacturing processes where rollers are subjected to hot rolling operations, such as shaping of steel sheets and plates.
- Microstructure: The microstructure of High Chromium iron rollers is typically composed of a matrix of austenite or martensite, depending on the heat treatment and alloying elements. These microstructural features contribute to the overall strength and thermal resistance of the material, allowing it to withstand thermal cycling and mechanical stresses during use.
- Application of Thermal Barrier Coatings: In some cases, additional thermal barrier coatings may be applied to High Chromium iron rollers to further enhance their heat resistance. These coatings can provide additional protection against thermal shock and prolong the service life of the rollers in demanding automotive manufacturing environments.
High Chromium iron rollers are resistant to high temperatures primarily due to their alloy composition, which promotes the formation of a protective oxide layer (chromia scale), their inherent oxidation resistance, good thermal stability of the microstructure, and sometimes the application of specialized coatings. These characteristics make them well-suited for handling the rigorous thermal conditions encountered in automotive manufacturing processes such as hot rolling operations.
What is the economic significance of using high chromium iron rolls in terms of improving productivity?
The economic significance of using High Chromium iron rolls in terms of improving productivity can be substantial for industries that rely on efficient and continuous manufacturing processes. Here are the key economic benefits:
- Increased Output and Throughput: High Chromium iron rolls are known for their durability and ability to withstand high pressures and temperatures. This allows for faster and more efficient rolling operations, which in turn increases the overall output and throughput of manufacturing processes. Higher productivity means more products can be produced within the same timeframe, maximizing the utilization of equipment and resources.
- Reduced Downtime and Maintenance Costs: The wear resistance of High Chromium iron rolls significantly reduces the frequency of roll changes and maintenance downtime. This translates into lower maintenance costs and less disruption to production schedules. Facilities can operate more consistently and reliably, minimizing lost production time and associated costs.
- Improved Efficiency: By maintaining dimensional accuracy and surface finish quality over longer periods, High Chromium iron rolls contribute to improved process efficiency. They enable smoother rolling operations with fewer defects and rework, optimizing the use of raw materials and reducing waste. This efficiency improvement directly impacts the cost per unit produced, enhancing profitability.
- Enhanced Product Quality and Consistency: High Chromium iron rolls help maintain consistent product quality by ensuring precise dimensions and smooth surface finishes in rolled products. This consistency reduces variability in product specifications and enhances customer satisfaction. Improved product quality also reduces the costs associated with quality control, rework, and customer returns.
- Competitive Advantage: Utilizing High Chromium iron rolls can provide a competitive advantage in the marketplace. Companies can offer reliable delivery schedules, consistent product quality, and competitive pricing due to improved productivity and efficiency gains. This strengthens their market position and allows them to capture more market share.
- Long-term Cost Savings: Although the initial investment in High Chromium iron rolls may be higher compared to other roll materials, the longer lifespan and reduced operational costs over time lead to significant long-term cost savings. These savings include lower maintenance costs, reduced energy consumption, and minimized downtime, contributing to improved profitability and return on investment.
- Sustainability and Environmental Benefits: High Chromium iron rolls contribute to sustainability efforts by reducing material waste, energy consumption, and emissions associated with manufacturing processes. Their longer lifespan and durability also decrease the need for frequent replacement and disposal, aligning with sustainable business practices.
The economic significance of using High Chromium iron rolls in terms of improving productivity encompasses increased output, reduced downtime and maintenance costs, improved process efficiency, enhanced product quality, competitive advantages, long-term cost savings, and sustainability benefits. These factors make High Chromium iron rolls a strategic investment for industries aiming to optimize their operations and achieve sustainable growth.