Cast steel roll is critical components in metalworking industries, particularly in rolling mills. They are known for their durability, wear resistance, and ability to withstand high mechanical stress. This article explores their properties, applications, manufacturing process, and maintenance.
Cast steel rolls are cylindrical tools used in rolling mills to deform and shape metal. They are made by casting molten steel into molds, followed by machining and heat treatment to achieve desired properties.
Different types of cast steel rolls are used depending on the application:
| Type | Composition | Primary Use |
| Indefinite Chilled Double Poured (ICDP) | High-carbon outer layer, ductile core | Hot rolling |
| High Chromium Steel Rolls | 12-22% chromium | Cold rolling, strip mills |
| Adamite Rolls | Nickel, molybdenum, chromium | General-purpose rolling |
Cast steel rolls must meet specific mechanical and thermal properties:
| Property | Importance |
| Hardness | Resists wear and deformation |
| Toughness | Prevents cracking under stress |
| Thermal Resistance | Withstands high rolling temperatures |
| Wear Resistance | Extends service life |
The production involves several stages:
Steel scrap and alloying elements are melted in electric arc furnaces or induction furnaces.
Molten steel is poured into molds, often using centrifugal casting for uniform density.
Rolls undergo quenching and tempering to enhance hardness and toughness.
Precision grinding ensures dimensional accuracy and surface finish.
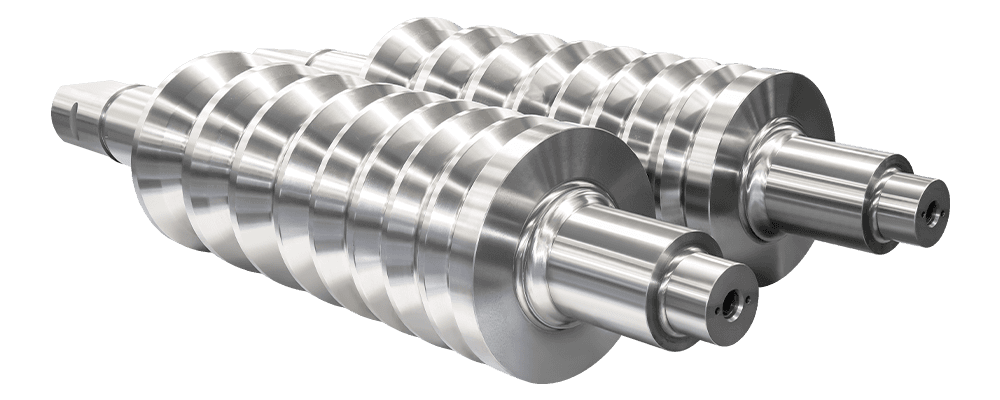
They are used in:
Proper maintenance includes:
| Issue | Solution |
| Surface Spalling | Adjust rolling parameters, improve cooling |
| Core Fractures | Optimize heat treatment process |
| Wear Unevenness | Regular regrinding and balancing |
Cast steel rolls are indispensable in metal forming. Understanding their properties, manufacturing, and maintenance ensures optimal performance and longevity in industrial applications.